Author: Conor Colgan
Technical Product Manager
ClearDATA
Data Breach Report: Cloud Storage Exposes 270,000 Users’ Private Information – March 25, 2020
Data Breach Exposes 14 Million Key Ring Users Data – April 6, 2020
Capital One Says Breach Hit 100 Million Individuals in U.S. – July 29, 2019
Headlines like those above have been becoming more prevalent over the last 6 months. Companies have seen sensitive data, including Protected Health Information (PHI), exposed publicly due to a misconfiguration in their Amazon S3 bucket. Often times, the data exposures are blamed on the S3 service itself, but the cause is more likely a lack of understanding of the service and its compliance controls.
Amazon S3 buckets are a location where you can store data, or objects, in a very flexible and scalable manner, using the standard HTTP protocol just like any website. With this flexibility comes responsibility. S3 can be configured to be privately accessible to only one user, or publicly available with all data available to anyone. In between those two extremes, customers can use access policies to provide extremely granular control of who can access the data located within a bucket. These policies do require some education and based on the amount of data exposed recently, it would seem that further education may be required.
Let’s take a look at some of the top misconfigurations in S3, and how you can correct them:
1. Permissions
Permissions for Amazon S3 buckets are commonly set via bucket policies. The permissions can be very powerful and granular, but they can also be very broad. Users often set broad permissions on S3 buckets in order to speed up the initial deployment of the environment. In that haste, someone might configure the bucket as Publicly Accessible, so all of the files hosted in it can be accessed by any part of the application. The problem with that is, anyone with an internet browser could find the bucket by name and now has access to your files.
TIP: Use the powerful policies available and restrict access to the bucket in order to prevent unauthorized access to the data.
2. Encryption
S3 offers three options for encrypting the objects located in buckets: Server-Side Encryption-S3 with keys managed by the S3 service itself, Server-Side Encryption-KMS with keys managed by the Amazon Key Management Service, and Server-Side Encryption-Customer with keys managed by the customer. Customers can use policies to ensure that objects uploaded into the bucket are encrypted, in order to protect the data from attackers or unauthorized personnel. When processing sensitive data, this is crucial to your business. It is highly recommended that encryption be implemented in order to protect your data from attackers or unauthorized personnel.
TIP: Use S3 Server-Side Encryption (SSE) and enable Amazon the ability to encrypt the data at the object level as it writes it to disks and decrypts it transparently for you when it is accessed.
3. Audit Logging
S3 buckets do not save audit logs by default, meaning if you do mistakenly open a bucket to the public you will not be able to review who accessed which files within your bucket. An access log record contains details about the requests made to a bucket. The request can include the request type, the resources specified in the request, and the time and date the request was processed. This information is incredibly powerful to ensure there is no unintended access to any data, and it should be turned on for all buckets that contain sensitive or important data.
TIP: Enable file level audit logging and save the logs to a central location, allowing you to perform an analysis of the logs in the event of a potential incident.
4. Data Classification
As discussed above, S3 buckets can be configured with public access. While you would not want to make the bucket public if it contains sensitive data, what if you wanted to provide static images for your website or build a simple and low-cost web application? S3 is the perfect use case for web service workloads, as it is extremely durable and low cost. Occasionally, data that may require public access resides in the same bucket as protected health information. This combination of differently classified data may put protected data at risk. Just as you would separate workloads on different servers, you should also separate workloads into different S3 buckets. Tags can be used as a different classification dimension, noting that bucket contains sensitive data or publicly available data. This helps your users understand what and how the buckets should and should not be used to ensure you both secure data and remain compliant. The use of tags also helps you monitor the buckets to ensure that all of the best practices are followed when hosting sensitive data in your AWS account.
TIP: Properly determine the classification of all data hosted in S3, such as “public”, or “confidential” or “protected”. Don’t mix confidential or protected data with public data.
What now?
Speaking of monitoring, how do you know your buckets are following the guidelines? Reviewing the current list of buckets to ensure they aren’t using broad access policies or encryption is not difficult, but it will take some time. After you complete that audit, how do you know that the new engineer you just hired isn’t creating buckets that don’t follow the guidelines? Those questions tend to create more questions. What if you are new to the cloud, or if you are part of a highly regulated industry such as healthcare? How can you ensure that your buckets are secure and compliant? As a CISO or IT leader, do you need to learn how to manage Amazon S3 bucket policies, log into all of your company’s AWS accounts, locate each bucket, and audit every policy? How often?
Our SaaS solution, ClearDATA Comply™, provides automation that will not only configure the settings mentioned above, but also enforce compliance with remediation throughout the lifecycle of your application called Automated Safeguards. ClearDATA Comply helps healthcare organizations monitor and manage their privacy and compliance obligations in the public clouds. As a HITRUST certified organization focused specifically on healthcare and life Sciences, we take an opinionated stance around how different regulations and standards apply to the public cloud.
With ClearDATA Comply, you have direct access to the AWS console while our automation enforces more than 150 technical controls and remediates non-compliant action, keeping you in an ideal state of compliance. ClearDATA offers Automated Safeguards for over 20 HIPAA eligible services from AWS, like S3; it’s available as part of our managed platform or as a standalone SaaS offering.
ClearDATA Comply also provides the ability to prove a culture of compliance in a matter of seconds, with near real-time reporting. Comply monitors assets, including S3 buckets, in an AWS customer’s environment to ensure they adhere to the rules and regulations, and visualizes the compliance status. ClearDATA has taken their experience working with different standards and regulations such as HIPAA, GxP, and GDPR, from multiple countries and mapped the S3 security controls to those frameworks, allowing customers to show compliance mapped to the appropriate regulations.
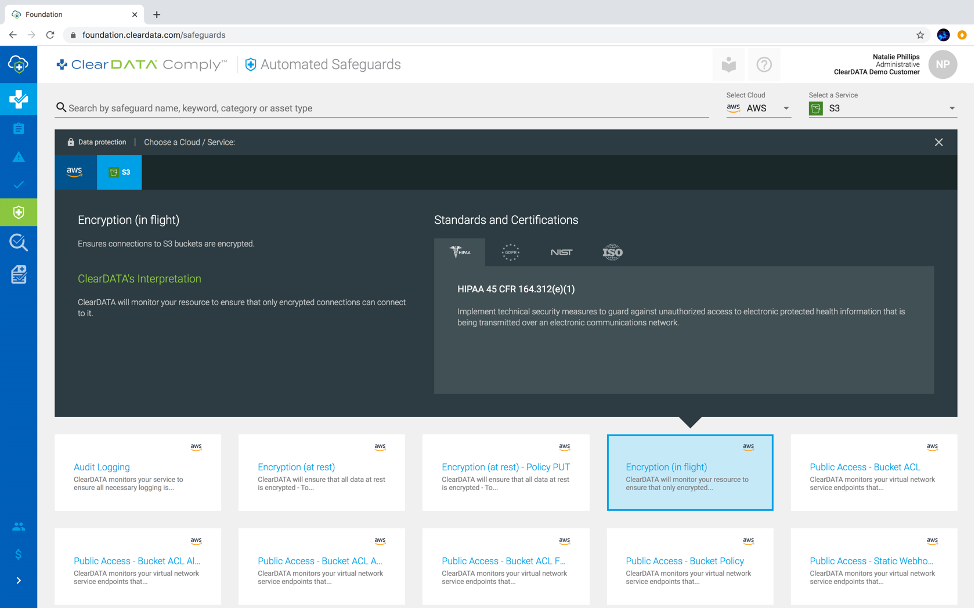
Figure 1: Based upon our opinionated stance of how regulations apply to the public cloud, ClearDATA Comply provides visibility into the list of technical controls enforced and how they map to different standards and regulations across different cloud services. This image shows which regulations apply to the technical control Encryption in flight, which must be enforced when using AWS S3 service with PHI.
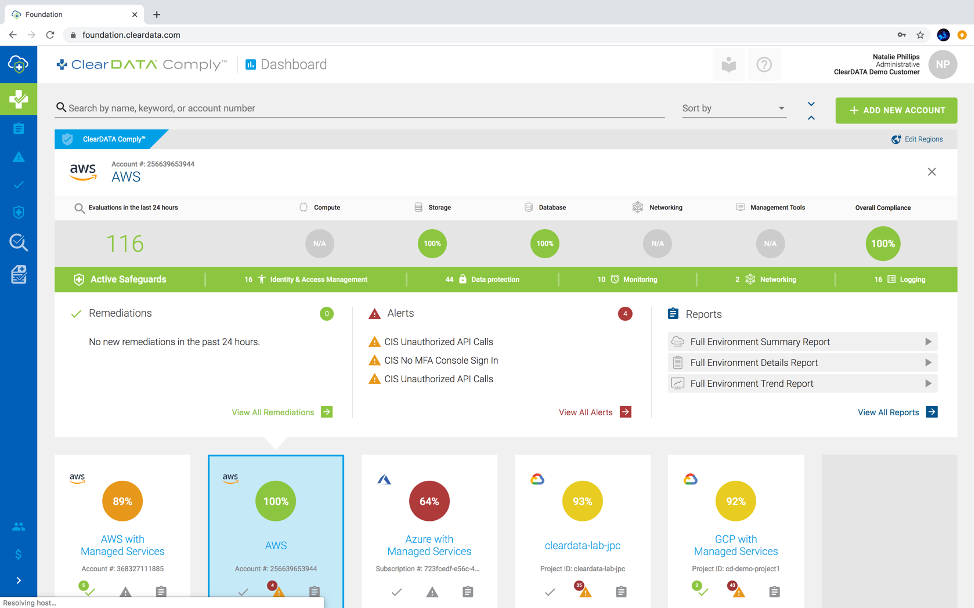
Figure 2: See a snapshot of your environment’s compliance status, with our at-a-glance compliance scoring for all of your environments.
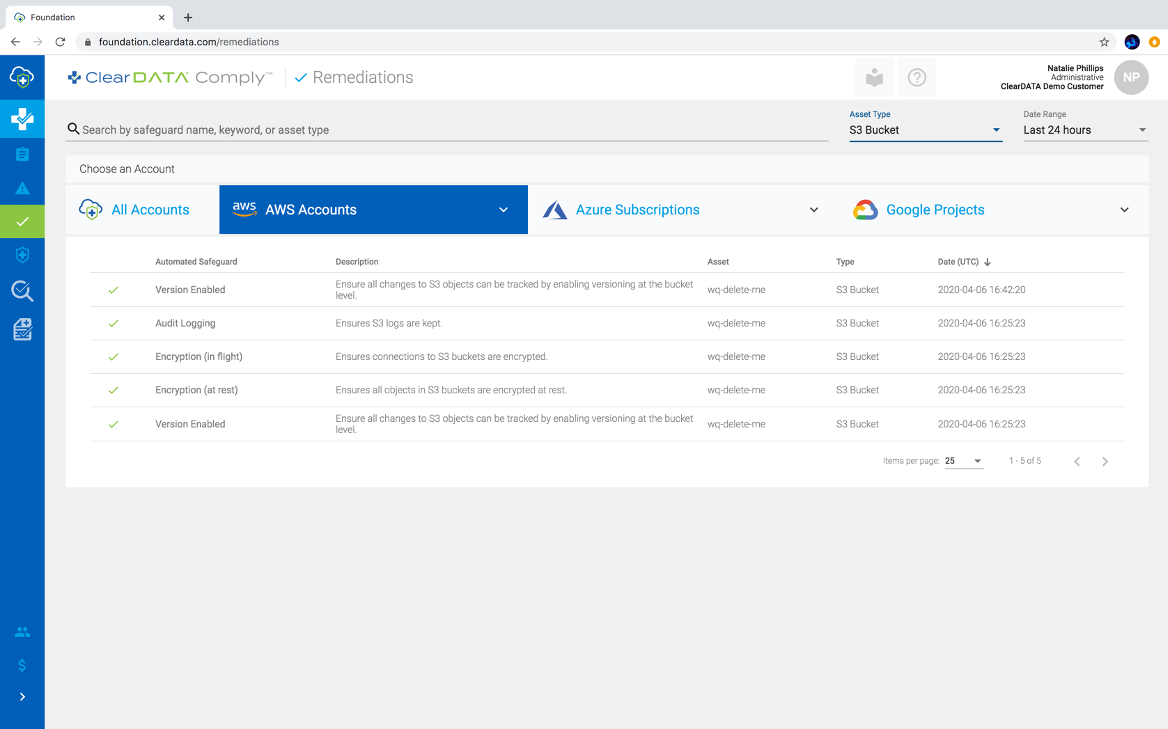
Figure 3: Within ClearDATA Comply, you can see all the remediations that took place over the last 24 hours, giving you visibility into common mistakes and what to avoid across your environments, or filtered to a specific service like S3, depicted in this view.
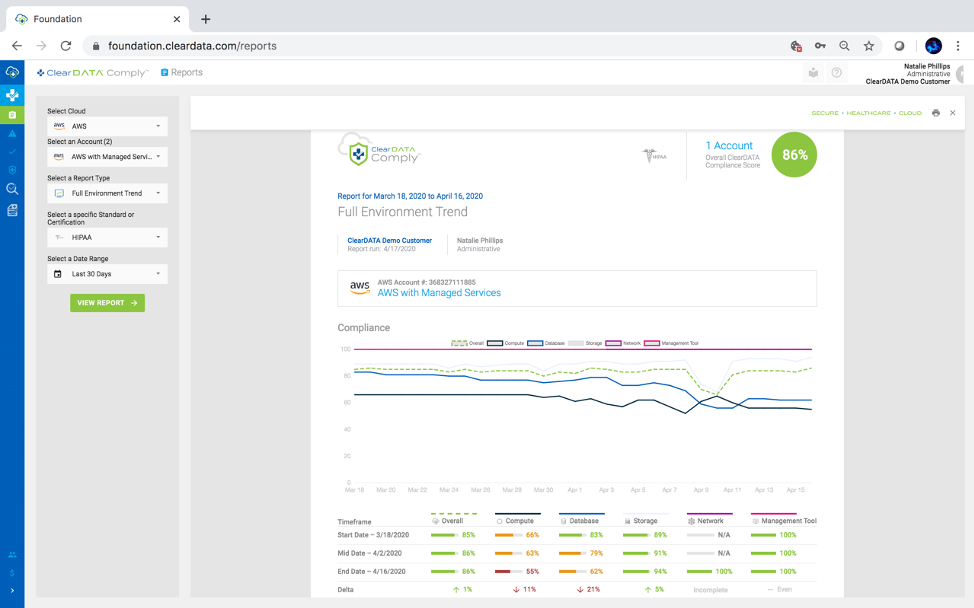
Figure 4: The ClearDATA Comply Trends Report monitors the compliance of other AWS assets, including EC2 and RDS, and maps the compliance over time. This powerful report can highlight your compliance monitoring policy, and how you have built a culture of compliance.
These reports allow you to create a culture of compliance and monitor your AWS assets, including S3 buckets, that contain your sensitive data. They also equip you to demonstrate to your leadership, auditors, and even customers that you are actively monitoring your cloud environment to ensure you are not the next headline.
Schedule a demo to see ClearDATA Comply in action.
Discover lessons learned from the Capital One breach that can help protect your organization from misconfigurations and insider threats.


